Wireless modules enable everything and speed up development
Release Time:
2020-08-28
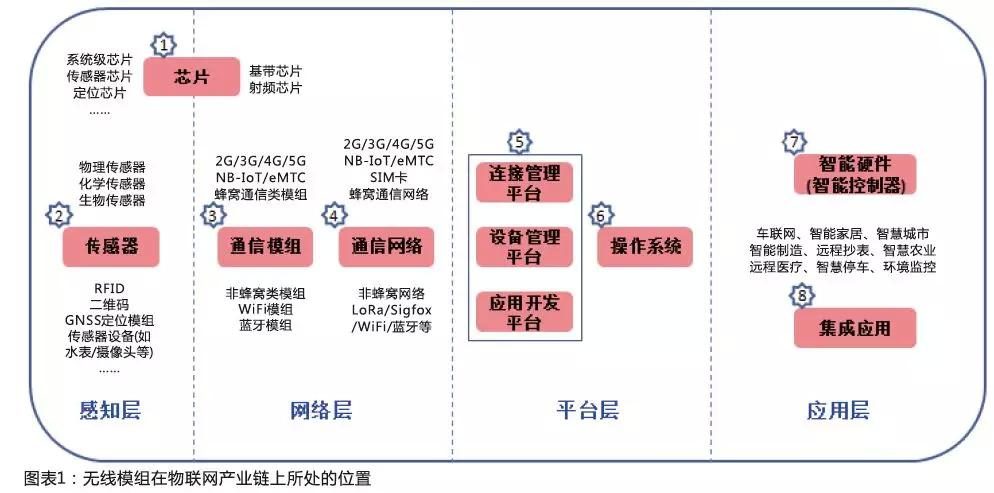
1 Introduction of wireless communication modules and industry chain analysisThe wireless module is a functional module that integrates chips, memory, power amplifier devices, etc. on a circuit board and provides standard interfaces. Various terminals can realize communication or positioning function
1 Introduction of wireless communication modules and industry chain analysis
The wireless module is a functional module that integrates chips, memory, power amplifier devices, etc. on a circuit board and provides standard interfaces. Various terminals can realize communication or positioning functions with the help of wireless modules. The wireless module is divided into "communication module" and "positioning module" according to the function. Relatively speaking, the application range of communication modules is wider, because not all IoT terminals need to have positioning functions. Communication modules include cellular communication modules (2G/3G/4G/5G/NB-IoT, etc.) and non-cellular communication modules (WiFi/Bluetooth/LoRa, etc.). The level of 10,000 is upgraded to the level of 100 million; positioning modules are mainly GNSS modules, including GPS modules, Beidou modules, etc.
The wireless communication module enables all kinds of terminal equipment to have the capability of networked information transmission. It is a key link connecting the perception layer and network layer of the Internet of Things. It belongs to the underlying hardware link and is irreplaceable.
The upstream industry of wireless modules is the production of raw materials such as baseband chips, radio frequency chips, positioning chips, capacitors and resistors, with a high degree of standardization. The baseband chip (communication chip) is the core, accounting for about 50% of the cost of materials, and has high technical barriers. At present, chip suppliers are mainly overseas manufacturers, such as Intel, Qualcomm, and MediaTek. Shoreline, Espressif, ZTE Microelectronics, etc., Beidou chip suppliers include Beidou Starcom, etc.
The downstream of wireless modules is generally IoT device manufacturers or IoT system integration service providers. Generally speaking, most IoT devices that need networking or positioning require wireless modules. The downstream is divided into various subdivided application fields, which are extremely scattered and often flow to various fields through intermediate distribution and consignment links. Module providers purchase upstream materials, are responsible for design and sales, and outsource production to third-party processing plants.
2 Core Values of Wireless Module Suppliers
Wireless modules have technical thresholds and customer thresholds, and are characterized by both standardization and customization. This determines that upstream chip manufacturers are too involved and uneconomical, and it is difficult for downstream customers to develop their own. The specific performance is as follows:
Wireless modules need to redesign and integrate a variety of chips and devices. Various communication protocols /standards, volume, interference, power consumption, special processes, etc. need to be considered, such as industrial-grade low temperature/high temperature resistance, vibration resistance, etc.;
The wireless module has the characteristics of customization and needs to meet the specific needs of different customers and different application scenarios. For example, the vehicle pre-installed module needs to meet the special specifications and standards of the automotive industry (such as ACE/SAE, etc.) ;
Customers are no longer satisfied that the communication module only undertakes the networking function, but also needs to integrate composite functions such as perception and front-end data processing capabilities, and even integrate Android system, cellular network, WiFi and Bluetooth functions, and GNSS.
3 The outbreak of the Internet of Things brings development space for wireless modules
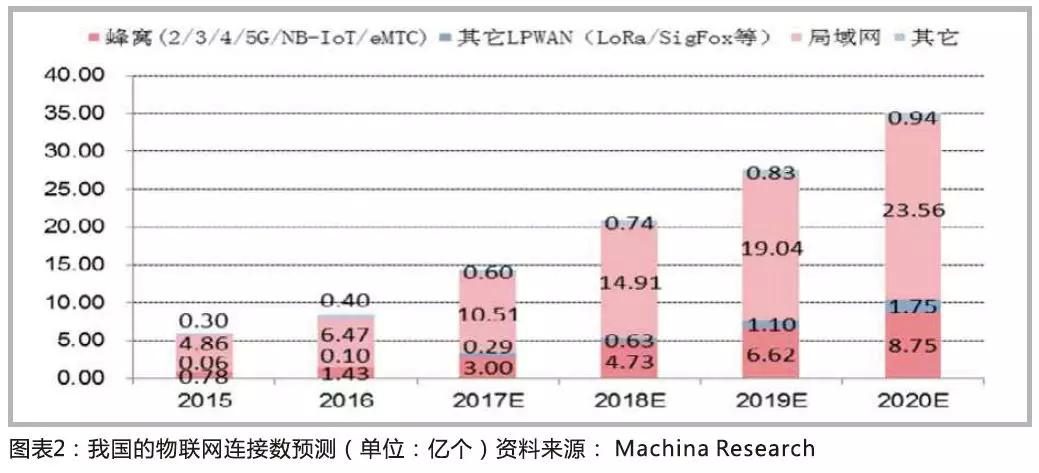
If the Internet of Things terminal wants to realize networking or positioning functions, it generally needs a wireless module. Under normal circumstances, for each increase in the number of IoT connections, 1-2 wireless modules need to be added; according to third-party data and industry research, a neutral forecast: in 2020, the number of IoT connections in China will increase by 317% compared with 2016, It will reach 3.5 billion, which will support the rapid increase in wireless module shipments.
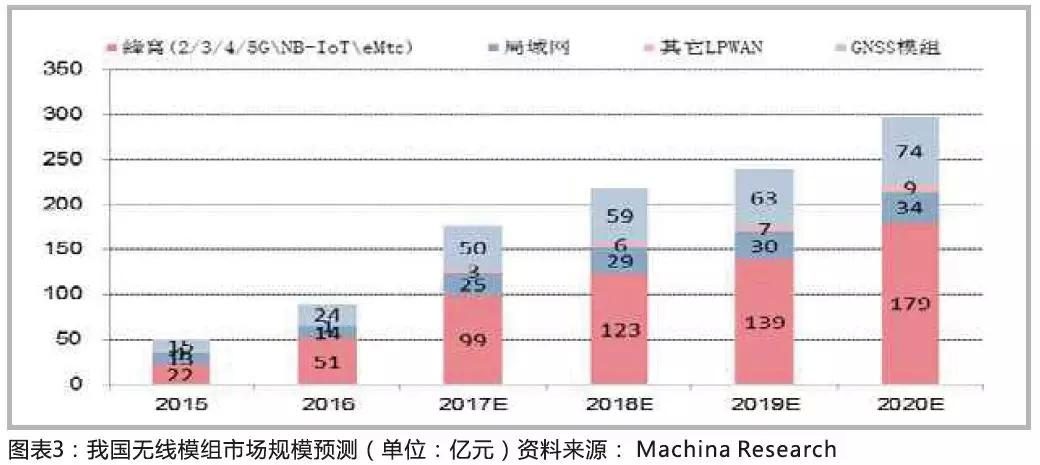
At present, non-cellular communication modules have the largest shipment volume of wireless modules, followed by positioning modules and cellular communication modules. Considering flexibility, the growth rate of cellular modules will be the fastest in the future, and the annual domestic shipments are increasing from tens of millions to 100 million. It is estimated that China's cellular module market will reach 9.9 billion yuan in 2017, an increase of 94% compared with 2016; according to ABI predicts that in 2021, global cellular module shipments will reach 365 million, with sales of 4.9 billion US dollars.
3.1 In the short term, the structural market scale growth brought about by the spillover of 4G technology to the M2M field
The penetration rate of 4G technology in mobile phones is already very high, but its application in the Internet of Things is just in its infancy. According to Ericsson's statistical analysis, by the end of 2016, the global M2M solutions using 2G accounted for about 50%, and the use of 4G LTE accounted for less than 10%. With technology upgrades and extensions, the proportion of 4G LTE will continue to grow. It is expected that M2M solutions using 4G LTE will become mainstream by 2019.
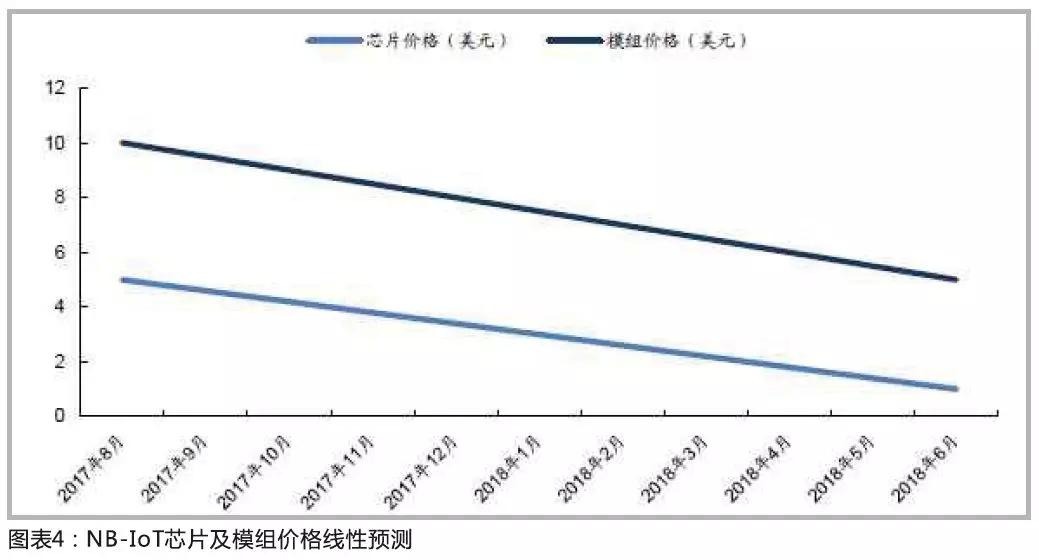
Regarding the price, there will be a downward trend in the long run, especially when the 4G module moves from testing to mass production, the price will drop rapidly, but with the improvement of integration, including the integration of Android system, WiFi and Bluetooth functions, and GNSS functions, the price of a single 4G module It is possible to rise further.
Policy promotion + market spontaneity, comprehensively promote the application of 4G technology in the M2M field. In terms of policies, the state promotes the popularization of 4G technology in key areas, such as the field of smart grid, to strengthen the upgrade of smart grid, to put forward new requirements for the integrity, reliability and real-time performance of meter information collection, and to introduce 4G wireless communication technology to the market. On the one hand, the emergence of new applications puts forward requirements for 4G communication technology, such as the smart POS machine market, which needs to embed 4G, Bluetooth modules and Android systems to complete a series of innovative applications.
3.2 In the medium term, the number of LPWAN modules will increase
The LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Internet of Things) module represented by NB-IOT/eMTC is expected to achieve large-scale commercial use by 2018 as the technology matures and costs decrease, and shipments will increase rapidly by then.
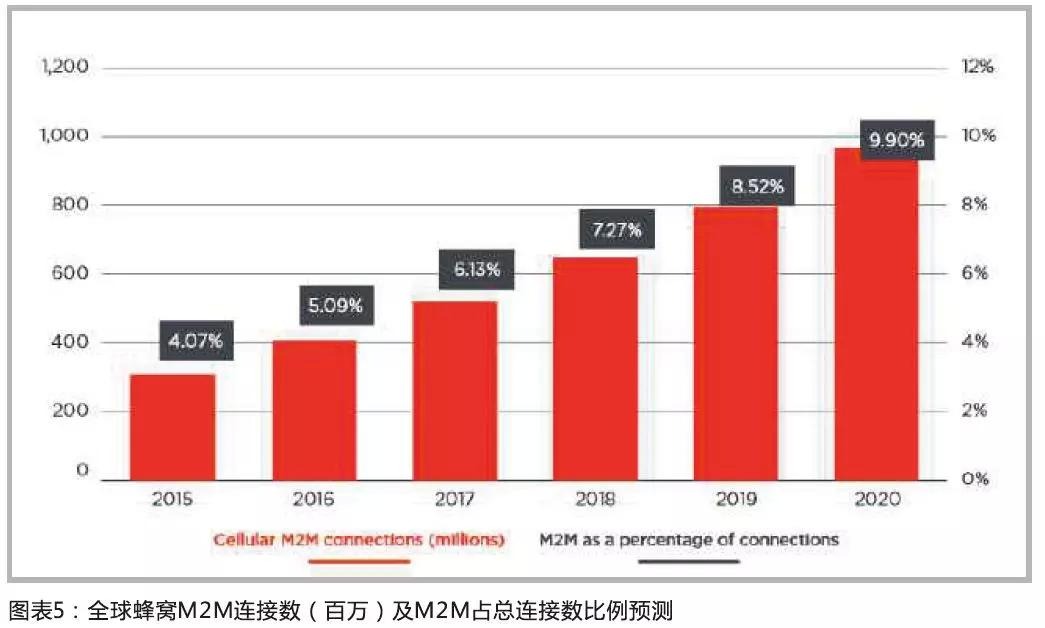
GSMA and CAICT jointly predict that China is currently the largest M2M market in the world, of which the number of cellular M2M connections is about 100 million, which is expected to increase to 350 million by 2020; and LPWA technology will provide an additional 730 million connections, making the total connections The number exceeds 1 billion. By 2025, 50% of the world's 28 billion connected devices are expected to be suitable for LPWA network connections.
3.3 In the long run, the overall rise of downstream applications
With the full-scale explosion of downstream applications of the Internet of Things, by 2020, the number of global Internet-connected devices is expected to reach tens of billions, and the era of Internet of Everything is expected to officially come.
According to GSMA estimates, by 2020, the number of global cellular IoT connections is expected to reach 1 billion, accounting for 10% of the global connections, with a compound growth rate of 26%. The number of M2M connections in China has reached about 1 billion, accounting for about 10% of the world's total.
4 Competitive landscape: foreign companies dominate, domestic companies compete
In the wireless communication module market, the current concentration is not high, and the first group company occupies about 30% of the global market share. With the rise of downstream applications and the expansion of the total market size, a number of high-quality module suppliers focusing on individual vertical application fields have begun to emerge. On the whole, a competitive situation has been formed in which the international and domestic first echelons lead, and the domestic second echelon gradually grows.
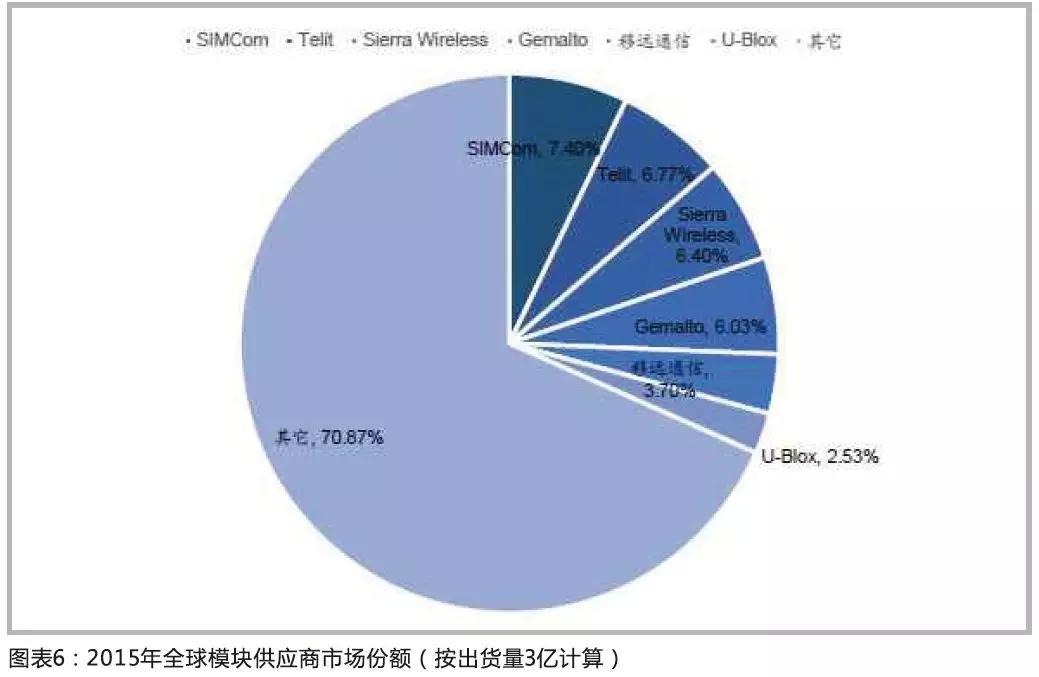
Based on ABI and Yole data, the global wireless module market is currently dominated by overseas companies, including Telit (Italy), Sierra Wireless (Canada), Gemalto (Netherlands), U-Blox (Switzerland), etc., and the cumulative share of the four companies exceeds 65%. . Domestic SIMCom and Quectel are also leading manufacturers of cellular communication modules. The former ranks first in the world in 2015, and the latter ranks fifth in the world.
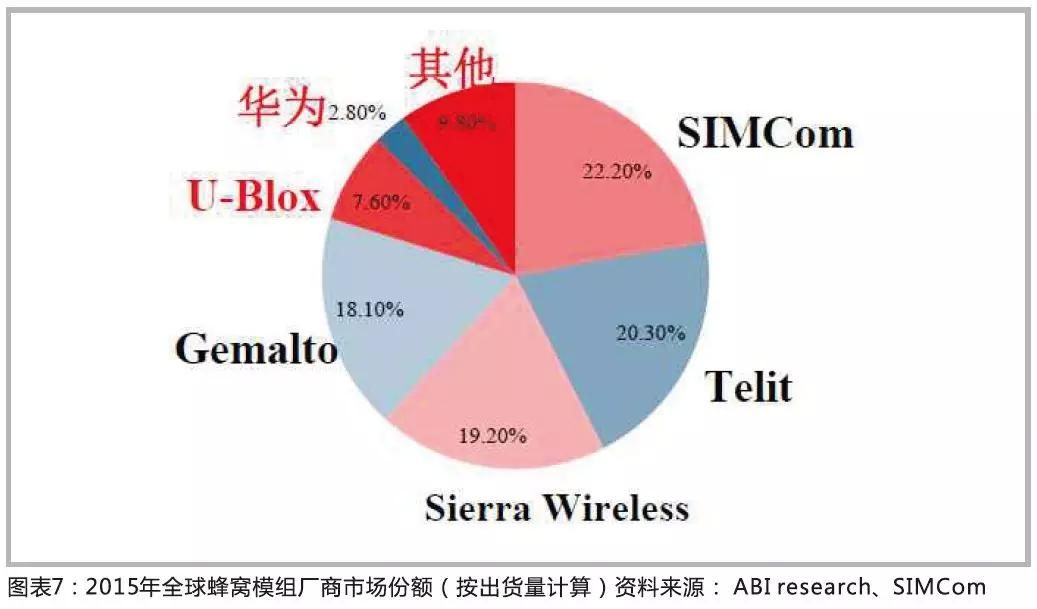
In addition to SIMCom and Quectel, domestic wireless module manufacturers also include Hangzhou Gubei, Fibocom, Shanghai Qingke, Longshang Technology, Youfang Technology, ZTE IoT, and China Mobile IoT.
The products of foreign wireless module companies are mainly high-end, such as 3G/4G modules and automotive-grade communication modules. Therefore, the gross profit margin of foreign companies is generally higher than 30%, while that of domestic companies is generally around 20%. Brand effect, sales model, customer structure, etc. determine the level of gross profit margin. The median net profit rate of domestic companies is 6% to 7%.
5 Analysis of Development Trends and Highlights
5.1 Communication modules will migrate from 2G to 4G and LPWAN
Currently, existing IoT devices mainly use 2G wireless modules, and the shipments of 4G and LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) NB-IoT and eMTC modules will grow rapidly in the future.
It is estimated that the share of 2G wireless modules will drop from about 80% in 2015 to 26% in 2020, and that of 4G wireless modules will rise from 2% in 2015 to 30%. NB-IoT and eMTC are expected to account for 2020 About 36.5%.
Reprinted from Huaqiang Microelectronics

Guangdong Joinet IOT Technology Co.,Ltd
Manufacturing Base:
Joinet Technology Park,No. 168 Tanlong North Road,Tanzhou Town,Zhongshan City,Guangdong Province,China
Pre Sales Hotline:19966308713 13823973022
Switchboard:0760-8663 0003 (transferred) 523
Pre Sales Email:sw@znaiot.com


Contact Us:
Looking forward to your call anytime